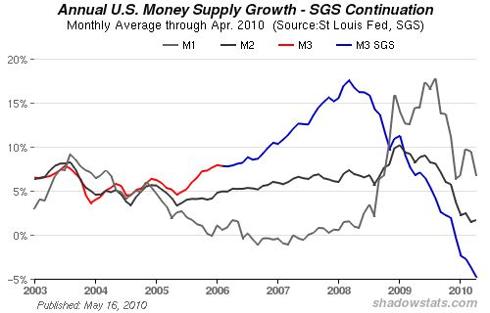
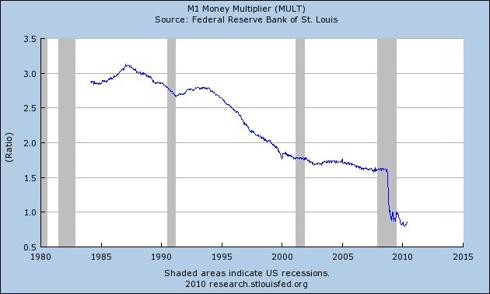
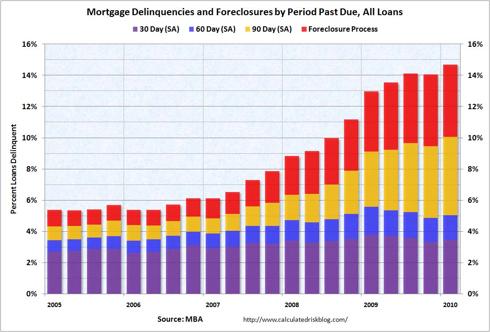
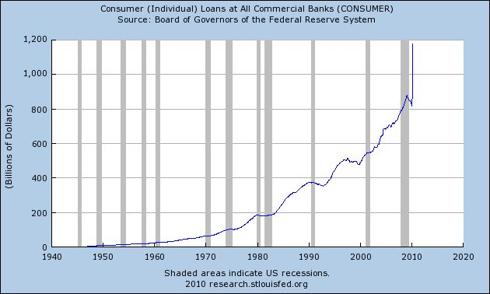
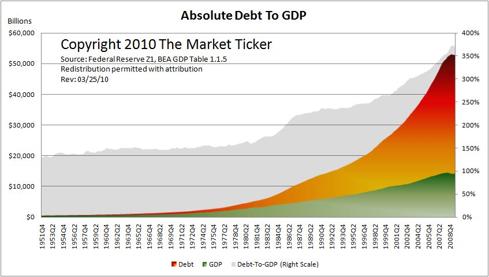
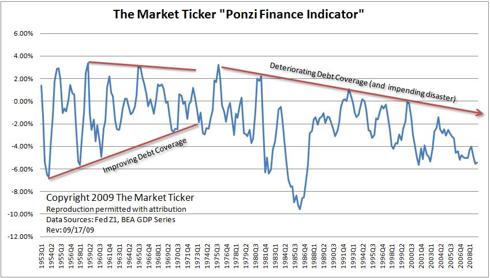
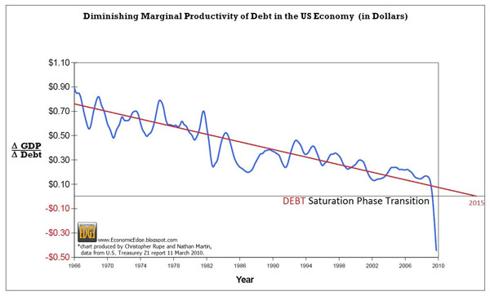
$1.2 Quadrillion Derivatives Market Dwarfs World GDP
June 24, 2010
AOL Finance
One of the biggest risks to the world’s financial health is the $1.2 quadrillion derivatives market. It’s complex, it’s unregulated, and it ought to be of concern to world leaders that its notional value is 20 times the size of the world economy. But traders rule the roost — and as much as risk managers and regulators might want to limit that risk, they lack the power or knowledge to do so.
ought to be of concern to world leaders that its notional value is 20 times the size of the world economy. But traders rule the roost — and as much as risk managers and regulators might want to limit that risk, they lack the power or knowledge to do so.
A quadrillion is a big number: 1,000 times a trillion. Yet according to one of the world’s leading derivatives experts, Paul Wilmott, who holds a doctorate in applied mathematics from Oxford University (and whose speaking voice sounds eerily like John Lennon’s), $1.2 quadrillion is the so-called notional value of the worldwide derivatives market. To put that in perspective, the world’s annual gross domestic product is between $50 trillion and $60 trillion.
To understand the concept of “notional value,” it’s useful to have an example. Let’s say you borrow $1 million to buy an apartment and the interest rate on that loan gets reset every six months. Meanwhile, you turn around and rent that apartment out at a monthly fixed rate. If all your expenses including interest are less than the rent, you make money. But if the interest and expenses get bigger than the rent, you lose.
You might be able to hedge this risk of a spike in interest rates by swapping that variable rate of interest for a fixed one. To do that you’d need to find a counter party who has an asset with a fixed rate of return who believed that interest rates were going to fall and was willing to swap his fixed rate for your variable one.
The actual cash amount of the interest rates swaps might be 1% of the $1 million debt, while that $1 million is the “notional” amount. Applying that same 1% to the $1.2 quadrillion derivatives market would leave a cash amount of the derivatives market of $12 trillion — far smaller, but still 20% of the world economy.
Getting a Handle on Derivatives Risk
How big is the risk to the world economy from these derivatives? According to Wilmott, it’s impossible to know unless you understand the details of the derivatives contracts. But since they’re unregulated and likely to remain so, it is hard to gauge the risk.
But Wilmott gives an example of an over-the-counter “customized” derivative that could be very risky indeed, and could also put its practitioners in a position of what he called “moral hazard.” Suppose Bank 1 (B1) and Bank 2 (B2) decide to hedge against the risk that Bank 3 (B3) and Bank 4 (B4) might fail to repay their debt to B1 and B2. To guard against that, B1 and B2 might hedge the risk through derivatives.
In so doing, B1 and B2 might buy a credit default swap (CDS) on B3 and B4 debt. The CDS would pay B1 and B2 if B3 and B4 failed to repay their loan. B1 and B2 might also bet on the decline in shares of B3 and B4 through a short sale.
At that point, any action that B1 and B2 might take to boost the odds that B3 and B4 might default would increase the value of their derivatives. That possibility might tempt B1 and B2 to take actions that would boost the odds of failure for B3 and B4. As I wrote back in September 2008 on DailyFinance’s sister site, BloggingStocks, this kind of behavior — in which hedge funds pulled their money out of banks whose stock they were shorting — may have contributed to the failures of Bear Stearns and Lehman Brothers.
It’s also the sort of conduct that makes it extremely difficult to estimate the risk of the derivatives market.
How Positive Feedback Loops Crash Markets
Another kind of market conduct that makes markets volatile is what Wilmott calls positive and negative feedback loops. These relatively bland-sounding terms mask some really scary behavior for investors who are not clued into it. Wilmott argues that a positive feedback loop contributed to the 22.6% crash in the Dow back in October 1987.
In the 1980s, a firm run by some former academics came up with the idea of portfolio insurance.
Their idea was that if investors are worried about their assets losing value, they can buy puts — the option to sell their investments at pre-determined prices. They can sell everything — which would be embarrassing if the market then started to rise — or they could sell a fixed proportion of their portfolio depending on the percentage decline in a particular stock market index.
This latter idea is portfolio insurance. If the Dow, for example, fell 3%; it might suggest that investors should sell 20% of their portfolio. And if the Dow fell 20%, it would indicate that investors should sell 100% of their portfolio.
That positive feedback loop — in which a stock price decline leads to more selling — boosts market volatility. Portfolio insurance causes more investors to sell as the market declines by, say 3%, which causes an even deeper plunge in the value of investors’ holdings. And that deeper decline leads to more selling. Before you know it, many investors are selling everything.
The portfolio insurance firm started off with $5 billion, but as its reputation spread, it ended up managing $50 billion. In 1987, that was a lot of money. So when that positive feedback loop got going, it took the Dow down 22.6% in a day.
The big problem back then was the absence of a sufficient number of traders using a negative feedback loop strategy. With a negative feedback loop, a trader would sell stocks as they rose and buy them as they declined. With a negative feedback loop strategy, volatility would be far lower.
Unfortunately, data on how much money has been going into negative and positive feedback loop strategies is not available. Therefore, it’s hard to know how the positive feedback loops have gained such a hold on the market.
But it is not hard to imagine that if a particular investor made huge amounts of money following a positive feedback loop strategy, other investors would hear about it and copy it. Moreover, the way traders get compensated suggests that it’s better for them to take more and more risk to replicate what their peers are doing.
Traders Make More Money By Following the Pack
There is a clear economic incentive for traders to follow what their peers are doing. According to Wilmott, to understand why, it helps to imagine a simplified example of a trading floor. Picture yourself as a new college graduate joining a bank’s trading floor with 100 traders. Those 100 traders each trade $10 million: They “win” if a coin toss lands on heads and “lose” if it lands on tails. But now imagine you’ve come up with a magic coin that has a 75% chance of landing on heads — you can make a better bet than the other 100 traders with their 50-50 coin.
You might think that the best strategy for you would be to bet your $10 million on that magic coin. But you’d be wrong. According to Wilmott, if the magic coin lands on a head but the other 100 traders flip tails, the bank loses $1 billion while you get a relatively paltry $10 million.
The best possible outcome for you is a 37.5% chance that everyone makes money (the 75% chance of you tossing heads multiplied by the 50% chance of the other traders getting a head). If instead, you use the same coin as everyone else on the floor, the probability of everyone getting a bonus rises to 50%.
When Traders Say ‘Jump,’ Risk Managers Ask ‘How High?’
Traders are a huge source of profit on Wall Street these days and they have an incentive to bet together and to bet big. According to Wilmott, traders get a bonus based on the one-year profits of those on their trading floor. If the trading floor makes big money, all the traders get a big bonus. And if it loses money, they get no bonus — but at least they don’t have to repay their capital providers for the losses.
Given that bonus structure, a trader is always better off risking $1 billion than $1 million. So if the trader, who is the king of the hill at the bank, asks a lowly risk manager to analyze how much risk the trader is taking, that risk manager is on the spot. If the risk manager comes back with a risk level that limits how big a bet the trader can take, the trader will demand that the risk manager recalculate the risk level lower so the trader can take the bigger bet.
Traders also manipulate their bonuses by assuming the existence of trading profits before they are actually realized. This happens when traders get involved with derivatives that will not unwind for 20 years.
Although the profits or losses on that trade have not been realized at the end of the first year, the bank will make an assumption about whether that trade made or lost money each year. Given the power traders wield, they can make the number come out positive so they can receive a hefty bonus — even though it is too early to tell what the real outcome of the trade will be.
How Trader Incentives Caused the CDO Bubble
Wilmott imagines that this greater incentive to follow the pack is what happened when many traders were piling into collateralized debt obligations. In Wilmott’s view, CDO risk managers who had analyzed a future scenario in which housing prices fell and interest rates rose would have concluded that the CDOs would become worthless under that scenario. He imagines that when notified of that possible outcome, CDO traders would have demanded that the risk managers shred that nasty scenario so they could keep trading more CDOs.
Incidentally, the traders who profited by going against the CDO crowd were lone wolves whose compensation did not depend on following the trading floor pack. This reinforces the idea that big bank compensation policies drive dangerous behavior that boosts market volatility.
What You Don’t Understand, You Can’t Properly Regulate
Wilmott believes that derivatives represent a risk of unknown proportions. But unless there is a change to trader compensation policies — one which would force traders to put their compensation at risk for the life of the derivative — then this risk could remain difficult to manage.
Unfortunately, he thinks that regulators aren’t in a good position to assess the risks of derivatives because they don’t understand them. Wilmott offers training in risk management. While traders and risk managers at banks and hedge funds have taken his course, regulators so far have not.
And if regulators don’t understand the risks in derivatives, chances are great that Congress does not understand them either.